Let's Know More About Blood Pressure

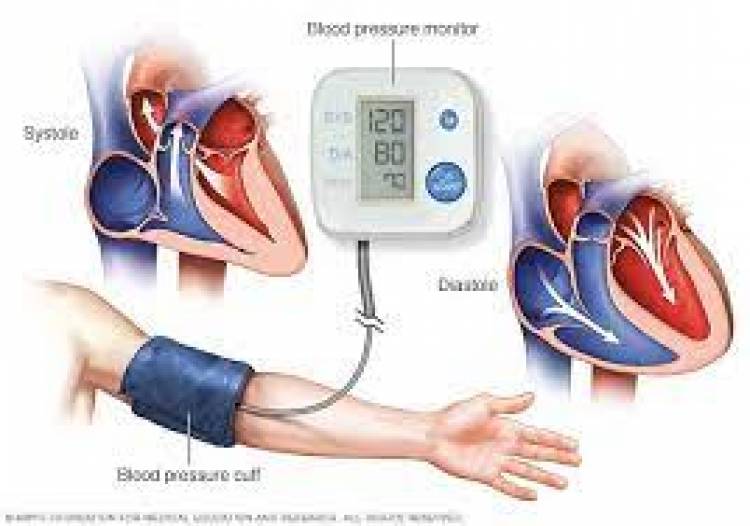
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, is blood pressure that is higher than normal. Your blood pressure changes throughout the day based on your activities. Having blood pressure measures consistently above normal may result in a diagnosis of high blood pressure (or hypertension). Blood pressure is written as two numbers. The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats. The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats.
Risk factors
There are several risk factors for hypertension. They are -
-
Modifiable risk factors include unhealthy diets (excessive salt consumption, a diet high in saturated fat and trans fats, low intake of fruits and vegetables), physical inactivity, consumption of tobacco and alcohol, and being overweight or obese.
-
Non-modifiable risk factors include a family history of hypertension, age over 65 years, and co-existing diseases such as diabetes or kidney disease.
Common symptoms
There are some common symptoms of hypertension. Hypertension is called a "silent killer". Most people with hypertension are unaware of the problem because it may have no warning signs or symptoms. For this reason, it is essential that blood pressure is measured regularly. When symptoms do occur, they can include early morning headaches, nosebleeds, irregular heart rhythms, vision changes, and buzzing in the ears. Severe hypertension can cause fatigue, nausea, vomiting, confusion, anxiety, chest pain, and muscle tremors. The only way to detect hypertension is to have a health professional measure blood pressure. Having blood pressure measured is quick and painless. Although individuals can measure their own blood pressure using automated devices, an evaluation by a health professional is important for the assessment of risk and associated conditions.
Related Problems
If not taken care of, it might lead to several problems. There can be many complications that can be faced by the people if they ignore this problem. Among other complications, hypertension can cause serious damage to the heart. Excessive pressure can harden arteries, decreasing the flow of blood and oxygen to the heart. This elevated pressure and reduced blood flow can cause:
-
Chest pain is also called angina.
-
A heart attack occurs when the blood supply to the heart is blocked and heart muscle cells die from lack of oxygen. The longer the blood flow is blocked, the greater the damage to the heart.
-
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to other vital body organs.
-
An irregular heartbeat can lead to sudden death.
Hypertension can also burst or block arteries that supply blood and oxygen to the brain, causing a stroke.
In addition, hypertension can cause kidney damage, leading to kidney failure.
Let’s know why is hypertension an important issue in low- and middle-income countries
The prevalence of hypertension varies across regions and country income groups. The WHO African Region has the highest prevalence of hypertension (27%) while the WHO Region of the Americas has the lowest prevalence of hypertension (18%).
The number of adults with hypertension increased from 594 million in 1975 to 1.13 billion in 2015, with the increase seen largely in low- and middle-income countries. This increase is due mainly to a rise in hypertension risk factors in those populations.

How can the burden of hypertension be reduced?
Reducing hypertension prevents heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage, as well as other health problems.
Prevention
1. Reducing salt intake (to less than 5g daily).
2. Eating more fruit and vegetables.
3. Being physically active on a regular basis.
4. Avoiding the use of tobacco.
5. Reducing alcohol consumption.
6. Limiting the intake of foods high in saturated fats.
7. Eliminating/reducing trans fats in the diet.
Management
1. Reducing and managing stress.
2. Regularly checking blood pressure.
3. Treating high blood pressure.
4. Managing other medical conditions.
If you liked this post, I’d be very grateful if you’d help it spread by emailing it to a friend or sharing it on Twitter or Facebook. Do not forget to like us on Facebook and follow us on Instagram. Send your entries too…
Thank You
Aashi Harita

























Comments (0)